Dans ce cours, nous allons voir la Fonction Logarithme népérien : Définition, sa relation avec la fonction exponentielle, Propriétés et des exercices d’ application sur comment résoudre les équations et inéquations.
Contenu
Fonction Logarithme Népérien
Définition : Fonction Logarithme Népérien
La fonction exponentielle est continue et strictement croissante sur ℝ.
Pour tout réel a de ] 0 ; + ∞ [ l’équation ex = a admet une unique solution dans ℝ.
Définition :
On appelle logarithme népérien d’ un réel strictement positif a, l’unique solution de l’équation ex = a. On la note ln a
La fonction logarithme népérien, est notée ln : ] 0 ; + ∞ [ ⟶ ℝ
x ⟼ ln x
Exemple :
L’équation ex = 6 admet une unique solution. Il s’agit de x = ln 6
A l’aide de la calculatrice, on peut obtenir une valeur approchée : x = 1,79
Remarque importante :
Les courbes représentatives de la fonction exponentielle et la fonction logarithme népérien sont symétriques par rapport à la droite d’équation y = x.
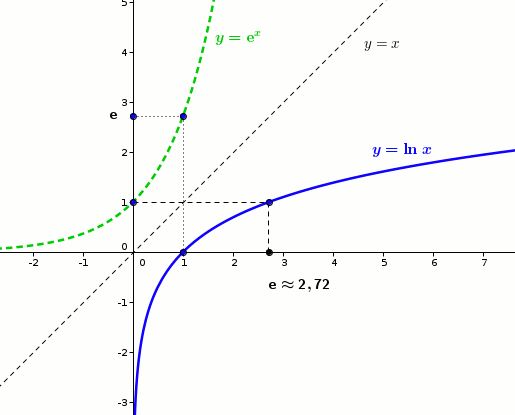
x = ea est équivalent à a = ln x avec x > 0
ln 1 = 0 ; ln e = 1 ; ln 1/e = ln e-1 = -1
Démonstrations :
ln 1 = 0 parce que e0 = 1
ln e = 1 parce que e1 = e
ln 1/e = ln e-1 = -1 ( 1/e = e-1 )
Pour tout x, ln ex = x
Si on pose y = ex , alors x = ln y = ln ex
Pour tout x strictement positif, eln x = x
Si on pose y = ln x , alors x = ey= eln x
Exemples :
eln7 = 7 ; eln5 = 5 et ln e4= 4
Autres Propriétés :
Pour tous réels x et y strictement positifs, on a :
a) ln x = lny ⟺ x = y ( Démonstration : x = y ⟺ eln x = eln y ⟺ ln x = ln y )
b) ln x < lny ⟺ x < y ( Démonstration : x < y ⟺ eln x < eln y ⟺ ln x = ln y )
Exercices d’application 1 : Résoudre une équation
Résoudre dans I les équations et inéquations suivantes :
a) ln x = 3 , I = ]0 ; + ∞[
b) ex+1 = 5, I = ℝ
c) 3ln x − 4 = 8 , I = ]0 ; + ∞[
Correction :
a) ln x = 3
⇔ ln x = lne3
⇔ x = e3 La solution est e3 .
b) ex+1 = 5
⇔ ex+1 = eln 5
⇔ x + 1 = ln5
⇔ x = ln5 − 1 La solution est ln5 − 1.
c) 3ln x − 4 = 8
⇔ 3ln x = 12
⇔ ln x = 4
⇔ ln x = ln e4
⇔ x = e4
La solution est e4.
Exercices d’application 2 : Résoudre une inéquation
Résoudre dans I les équations et inéquations suivantes :
a) ln(6x − 1) ≥ 2 , I = ]1/6 ; + ∞[
b) ex + 5 > 4ex , I = ℝ
Correction :
a) ln(6x − 1) ≥ 2
⇔ ln(6x − 1) ≥ ln e2
⇔ 6x − 1 ≥ e2
⇔ x ≥ (e2 + 1 )/6
L’ensemble solution est donc [ (e2 + 1 )/6 ; + ∞[
b) ex + 5 > 4ex
⇔ ex − 4ex > −5
⇔ −3ex > −5
⇔ ex < -5/-3
⇔ ex < 5/3
⇔ ex < eln( 5/3)
⇔ x < ln( 5/3)
L’ensemble solution est donc ] -∞ ; ln( 5/3) [
Propriétés de la fonction logarithme népérien
Théorème :
Pour tous réels x et y strictement positifs, on a : ln( x × y ) = ln x + ln y
Démonstration :
eln( x× y) = x × y = eln x × eln y = eln x+ln y
Donc ln( x × y) = ln x + ln y
Formules :
a) ln 1 /x = − ln x
b) ln x/y = ln x − ln y
c) ln x1/2 = 1/2 ln x
d) ln xn = n ln x avec n entier relatif
Démonstrations :
a) ln 1/x – ( – ln x ) = ln 1/x + ln x = ln ( 1/x x x ) = ln 1 = 0
b) ln x/y = ln ( x x 1/y ) = ln x + ln ( 1/y ) = ln x – ln ( y )
c) 2ln x1/2 = ln x1/2+ ln x1/2 = ln( x1/2 × x1/2 ) = ln x
Exercice d’ application :
1) Résoudre dans ! l’équation : 8x = 3
2) Résoudre dans ] 0;+∞ [ l’équation : x7 = 5
3) Tu as 9 augmentations successives de t % correspondent à une augmentation globale
de 60 %. Donner une valeur approchée de t.
Correction :
1)
8x = 3
⇔ ln 8x = ln3
⇔ x ln8 = ln3
⇔ x = ln3 / ln8
La solution est ln3 / ln8
2) Comme x > 0 , on a :
x7 = 5
⇔ ln ( x7 ) = ln 5
⇔ 7 ln x = ln 5
⇔ ln x = 1/7 ln5
⇔ ln x = ln ( 51/7 )
⇔ x = 51/7
La solution est : 31/5
3)
Le problème revient à résoudre dans ] 0;+∞ [ l’équation : ( 1 + t/100 )9= 1,6
( 1 + t/100 )9= 1,6
⇔ ln ( 1 + t/100 )9 = ln ( 1,6 )
⇔ 8. ln ( 1 + t/100 ) = ln ( 1,6 )
⇔ ln ( 1 + t/100 ) = 1/8 ln ( 1,6 )
⇔ ln ( 1 + t/100 ) = ln ( 1,61/9 )
⇔ 1 + t/100 = 1,61/9
⇔ t = 100.(1,61/9 – 1 ) ≈ 5.3 ( Pour calculer 1,61/9 tu peux utiliser notre Calculatrice en ligne gratuite )
Une augmentation globale de 60 % correspond à 9 augmentations successives d’environ 5,3 %.
